Ketogenic Diet
The Absolute Beginner’s Guide to Keto
What is the Ketogenic Diet?
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat diet with very low carbohydrates and moderate protein. It can be helpful for people trying to lose weight, lower blood sugar, improve brain function, or improve metabolism. This diet changes how your body makes energy, from using sugar as fuel to using fat as fuel. Flipping this switch in the cells can allow the body to function more smoothly and go into a healing state.
Here, you will learn how to decide if keto is right for you, how to get started on a keto diet, what to eat, what not to eat, and what to expect from going keto.
Understanding the Keto Diet for You
The keto diet works by allowing your body to shift into a different way of burning energy — to primarily burn fat instead of sugar.
When you burn fat as your primary energy, you are in a metabolic state called ketosis. While in ketosis, your liver breaks down fat into molecules called ketones. These ketones become the fuel for all cells in the body.
Why It Matters
Just as it sounds, burning fat as the main source of energy can:
-
- Cause fat loss
- Support better blood sugar balance
- Improve several chronic conditions
How Do You Enter Ketosis?
To get the body into ketosis, you must carefully manipulate macronutrients —
the three main nutrient types in your food:
-
- Carbohydrates
- Protein
- Fat
The amount of each of these macronutrients (or “macros”) that you eat daily will determine your ability to get into and maintain ketosis.
General Keto Macronutrient Breakdown
-
- Carbohydrates: 5% of calories or less
- Protein: 20–25% of calories
- Fat: 70–75% of calories
It is common for this to work out to about 25–50 grams of carbohydrate per day.
Foods That Affect Ketosis
Carbohydrates like:
-
- Bread, pasta, whole grains
- Potatoes, sugary sodas, juices
- Even whole fruits and some vegetables
…all break down into sugars and have a large impact on blood sugar levels.
Although protein can also affect blood sugar levels, it has much less impact than carbohydrates.
Ketogenic Diet Types
There are several types of ketogenic diets that are used for different purposes. Here they are:
Conscious Keto: This is a health-conscious version of the classic keto diet, in which you follow the same macro pattern daily and track your food intake. You choose high-quality, organic, whole foods and avoid processed foods.
High-protein Keto: High-protein keto allows for 30–35% or more calories from protein and less from fat. This may be a good option if you have higher protein needs such as during chemotherapy or radiation, when recovering from surgery, or for other reasons.
Cyclical Keto: On cyclical keto, you cycle between high-carb and strict keto. This may be useful for people in training or who adjust their macros around hormonal shifts.
Targeted Keto: Targeted keto is like cyclical keto, but the carbs are timed before workouts. These carbs are burned up during your workout, so it’s easier to stay in ketosis.
Modified Keto: Modified keto allows for more carbs and less fat. It creates a hybrid metabolism in which the body is burning both fat and sugar. This may be easier to implement for some people since it is less strict. It is also a way forward for people whose bodies do not adapt to a full ketogenic diet.
Which of these styles you choose or combine depends on your needs and goals.
Potential Health Benefits
Keto is most well-known for weight loss, but this diet has many other health supportive effects. When implemented with the right kinds of fats, the diet can be strongly anti-inflammatory and cause a profound metabolism reset. These effects together are likely responsible for its health benefits. It takes a couple of weeks for the body to become well-adapted to the diet. At that point the benefits begin to show.
Supports Weight Loss
It’s no surprise that a goal of weight loss leads many people to want to try keto. The ketogenic diet switches the body into fat-burning mode, burning both dietary fat as well as body fat. This significantly reduces body weight and waist measurement 1✓.
Being in ketosis also greatly increases satiety. Fat and protein are much more filling than carbohydrates, and ketones turn off the hunger signal. As a result, many people experience less hunger during ketosis. This can make intermittent fasting occur very naturally, which enhances the health benefits of the diet 2✓.
How much weight you might lose on keto is very individual. During the first week, the body is adjusting by burning off all the stored sugar in the liver. This releases a lot of water, and water is heavy! So, the weight loss in week one can be anywhere from 0.5 to 4.5 kilos. Weight loss greatly slows down after the first week. For example, the average weight loss in one group was 9 kg after 3 months in ketosis 3✓.
Strength training can ensure you build or maintain muscle during your keto diet. Muscle burns more calories at rest and serves to further regulate blood sugar. Also, remember that muscle weighs more than fat. If your keto diet has you burning fat and maintaining muscle, your change in size and shape are equally important success indicators as your weight.
Helps Regulate Blood Sugar Naturally
The keto diet is often used to regulate blood sugar and increase insulin sensitivity. With these effects, it can be a natural fit for those with type 2 diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). The diet can achieve notable decreases in fasting blood glucose, glycated hemoglobin, and HOMA-IR levels, which are all indications of better blood sugar management (1✓, 3✓, 4✓).
Even though the keto diet emphasizes high fat intake, it actually improves lipid levels such as reducing triglycerides and increasing HDL. It is the radically decreased carb intake that keeps insulin from being overproduced that is key to reinvigorating blood sugar control. The one-two punch of high fat and low carb creates a deeply healing reset on metabolism (4✓, 5✓).
Healthy Brain Function
Keto for childhood epilepsy is quite a common therapy today. Various types of keto diets are considered effective for children with epilepsy. Keto diets for children tend to be stricter than those for epileptic adults. This may be why low-carb diets have been found to be a bit less effective for adults with seizures than for children. When adults have the support to implement a stricter keto diet, especially in combination with other measures, individuals may find more personal success (6✓, 7✓).
As mentioned, one of the effects of keto is to reduce inflammation. This includes brain inflammation, which is a major factor in depression, schizophrenia, dipolar disorder, and dementias. Brain inflammation reduction in addition to the beneficial brain cell metabolism shift also provides neuroprotection in relation to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s 8✓.
Cancer Metabolism
Because cancer cells cannot use ketones as energy, the keto diet is used by many cancer patients to turn the body’s metabolism against cancer. When the body is making energy that all the body’s cells can easily use, but cancer cells cannot, that tactic might be considered as a strong self-care measure against cancer. This approach is most well known in relation to brain tumors, using a fully ketogenic diet. It has also become popular in the complementary therapy of non-brain cancers to try a modified keto diet that is mostly plant-based (aka ketotarian). A cyclical keto diet is sometimes used around chemotherapy cycles to reduce side effects. While formal research is slow to emerge in this area, the collective clinical experience of practitioners and patients continues to very actively develop and productively evolve (9✓, 10✓, 11✓).
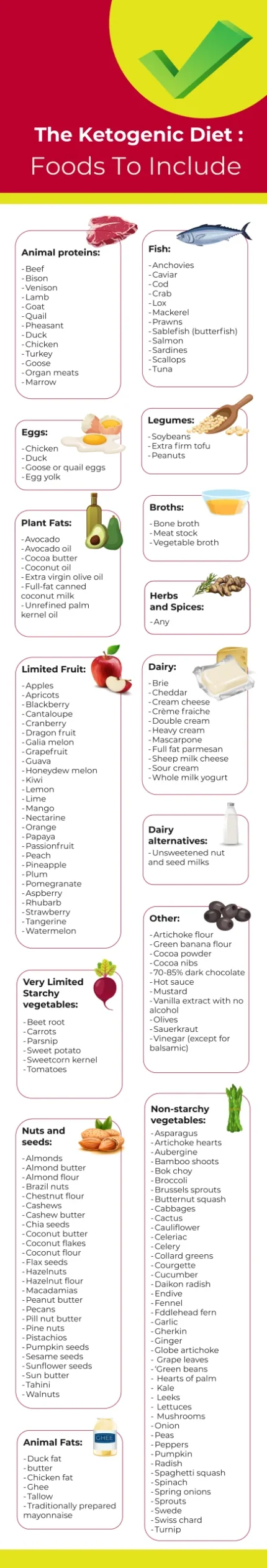
Foods To Include
The key is to eat primarily fat and an absolute minimum of carbohydrates with moderate protein. What does that look like in food? Here is a shopping guide:
-
- Animal Proteins: Beef, bison, venison, lamb, goat, quail, pheasant, duck, chicken, turkey, goose, organ meats, marrow
- Fish: Anchovies, caviar, cod, crab, lox, mackerel, prawns, sablefish (butterfish), salmon, sardines, scallops, tuna
- Eggs: Chicken, duck, goose, or quail eggs, egg yolk
- Legumes: Soybeans, extra firm tofu, peanuts
- Limited Fruit: Apples, apricots, blackberry, cantaloupe, cranberry, dragon fruit, galia melon, grapefruit, guava, honeydew melon, kiwi, lemon, lime, mango, nectarine, orange, papaya, passionfruit, peach, pineapple, plum, pomegranate, raspberry, rhubarb, strawberry, tangerine, watermelon
- Non-Starchy Vegetables: Asparagus, artichoke hearts, aubergine, bamboo shoots, bok choy, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, butternut squash, cabbages, cactus, cauliflower, celeriac, celery, collard greens, courgetti, cucumber, daikon radish, endive, fennel, fiddlehead fern, garlic, gherkin, ginger, globe artichoke, grape leaves, green beans, hearts of palm, kale, leeks, lettuces, mushrooms, onion, peas, peppers, pumpkin, radish, spaghetti squash, spinach, Spring onions, sprouts, swede, Swiss chard, turnip
- Dairy: Brie, cheddar, cream cheese, crème fraiche, double cream, heavy cream, mascarpone, full fat parmesan, sheep milk cheese, sour cream, whole milk yogurt
- Dairy Alternatives: Unsweetened nut and seed milks
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, almond butter, almond flour, Brazil nuts, chestnut flour, cashews, cashew butter, chia seeds, coconut butter, coconut flakes, coconut flour, flax seeds, hazelnuts, hazelnut flour, macadamias, peanut butter, pecans, pill nut butter, pine nuts, pistachios, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, sunflower seeds, sun butter, tahini, walnuts
- Animal Fats: Duck fat, butter, chicken fat, ghee, tallow, traditionally prepared mayonnaise
- Plant Fats: Avocado, avocado oil, cocoa butter, coconut oil, extra virgin olive oil, full-fat canned coconut milk, unrefined palm kernel oil
- Herbs and Spices: Any
- Broths: Bone broth, meat stock, vegetable broth
- Very Limited Starchy Vegetables: Beet root, carrots, parsnip, sweet potato, sweetcorn kernel, tomatoes
- Other: Artichoke flour, green banana flour, cocoa powder, cocoa nibs, 70–85% dark chocolate, hot sauce, mustard, vanilla extract with no alcohol, olives, sauerkraut, vinegar (except for balsamic)
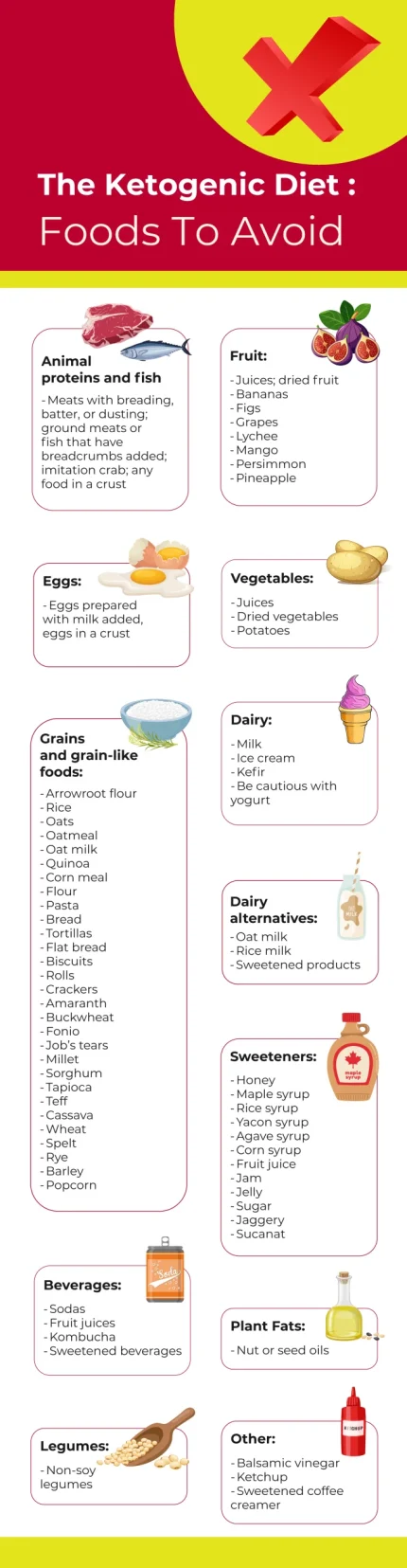
Foods To Avoid
The main thing to avoid is food with significant carb content that might throw you out of ketosis. Here are some guidelines:
-
- Animal Proteins and Fish: Meats with breading, batter, or dusting; ground meats or fish that have breadcrumbs added; imitation crab; any food in a crust
- Eggs: Eggs prepared with milk added, eggs in a crust
- Legumes: Non-soy legumes
- Grains and Grain-like Foods: Arrowroot flour, rice, oats, oatmeal, oat milk, quinoa, corn meal, flour, pasta, bread, tortillas, flat bread, biscuits, rolls, crackers, amaranth, buckwheat, fonio, Job’s tears, millet, sorghum, tapioca, teff, cassava, wheat, spelt, rye, barley, popcorn
- Fruit: Juices; dried fruit, bananas, figs, grapes, lychee, mango, persimmon, pineapple
- Vegetables: Juices; dried vegetables; potatoes
- Dairy: Milk, ice cream, kefir, be cautious with yogurt
- Dairy Alternatives: Oat milk, rice milk, sweetened products
- Plant Fats: Nut or seed oils
- Sweeteners: Honey, maple syrup, rice syrup, yacon syrup, agave syrup, corn syrup, fruit juice, jam, jelly, sugar, jaggery, sucanat
- Beverages: Sodas, fruit juices, kombucha, sweetened beverages
- Other: Balsamic vinegar, ketchup, sweetened coffee creamer
Supplements to Take
Supplements may not be necessary especially on a short-term ketogenic diet. However, since it is an alternative form of metabolism, many people benefit from some kind of supplementation to support the body in efficient ketosis and balance during longer-term use of the diet. Here are some supplements to consider:
-
- Electrolytes: Particularly sodium can get low during a ketogenic diet. While some people simply add a lot of sea salt to their foods, others may find it necessary to supplement with a sodium-heavy electrolyte product. LINK TO (or name) IN-STORE PRODUCT
- Medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) oil: MCT oil is very efficient for the body to make ketones. So many people supplement their keto diet with extra MCT oil, usually added to meals or shakes. LINK TO (or name) IN-STORE PRODUCT
- Digestive Enzymes: With such a high fat content, the ketogenic diet can be extra work for the digestive system. Taking a broad-spectrum digestive enzyme that is high in lipase can help you break down the fat in each meal. LINK TO (or name) IN-STORE PRODUCT
- Bile Flow Support: Again, this is with the high fat content of the diet in mind. To digest fat properly, we need adequate bile flow. Bile emulsifies our dietary fat and makes it absorbable. You might consider Malic Acid to thin the bile and make it more flowable. LINK TO (or name) IN-STORE PRODUCT
Supplements to Avoid
Omega-3 fatty acids like fish oil, krill oil, flax oil, and algal oil: The ketogenic diet pushes the body into a catabolic state over time. That is the active, breaking-down state we are already in during the day and during exercise. Fatty acids also push us into a catabolic state. So it’s counterintuitive to take omega-3 fatty acids with a ketogenic diet as it may lead you more quickly or more deeply into an imbalanced overly catabolic state.
Getting Started
The ketogenic diet, especially a strict and continuous one, is an extreme metabolic gesture. You may wish to consult a knowledgeable practitioner before beginning any keto diet. You may also wish to consult your pharmacist to check if the keto diet will negatively impact you taking any of your medications or if any of your medications will impact the keto diet.
Finally, it’s important that you understand the ins and outs of the diet for yourself. You will probably be using at least a book or an app to support yourself in the keto diet. Ahead of that, here is a primer.

Understand Your Keto Diet
With the keto diet, planning is everything. You will want to know for yourself how the diet works. Determine what foods will be allowed and not allowed on your version of the diet. And know how to monitor yourself. You may wish to obtain a ketogenic cookbook geared for your style of keto diet.
If you will be starting a full ketogenic diet, that is if you are planning to go into ketosis, you will absolutely need to monitor your ketones regularly. This may be observed at first with urine testing in the first couple of weeks. However, when the body is keto-adjusted it is best to measure ketones in the blood. Many glucose monitors can measure ketones as well. There are two different test strips for glucose and ketones. It’s great to measure both and know what your targets are.
Calculate Your Macros
A ketogenic cookbook or calculator can help you determine the best macros for your weight and for your therapeutic purpose. Remember that macros include the total calories per day and the amount of fat, carbohydrate, and protein those calories are made of. This very personal formula will result in your amount of success and how well you feel on the keto diet. So, it’s very worthwhile to take the time to dial it into the best guess possible.
That’s right. It’s a guess that you will be able to tweak based upon your monitoring.
Go Food Shopping
Clear the way in your pantry for your keto foods. Move high-carb foods to another shelf so you can very easily see what ingredients you have on hand for your keto diet. If your family is not joining you on a keto diet, let your family know what you are planning and determine how that might change the mealtime experience for everyone.
Make a shopping list from your keto cookbook or app. Visit your most well-stocked store specializing in healthy keto food and bring your shopping list with you. Load up on keto foods you will keep in the pantry, refrigerator and freezer.
Plan Your Meals
Based on the foods you find at the store — what is in season, what is on sale, what you prefer — you will make your meal plan. Plan one week of keto meals using your cookbook and/or keto app. Also plan the times of day you will eat. The keto diet is so different from the way most people at that it can be disorienting at first.
You don’t want to come to a mealtime and have no idea what to eat. So, write it all down. Also, plan when you will be cooking each meal. Will you cook some things ahead and freeze or refrigerate them? Will you do some food prep ahead of time to make cooking go faster?
Look at your calendar and see what you have planned for the week. Are you going out to dinner? Do you have a party? Make keto plans for these occasions so you are easily prepared.
Also on your calendar, note when in the week you will make next week’s meal plan and when you will go shopping again. Giving yourself space and time to do the diet is one key to success. It’s a diet that has planning as an integral part of its practice.
Monitor Your Progress and What You Eat
There are typically two measures of progress on the keto diet. The first measure is whether you are in ketosis and how deeply you are in ketosis. Know your target ranges for ketones and glucose. Plan when you will measure these and track the results.
The second measure of progress depends on what you are trying to achieve. It may be a follow-up blood test with your doctor showing lower inflammation or lower blood sugar parameters. It may be your weight or waist circumference. It may be your brain function or pain level. Determine what it is for you and plan to note down your measurements on a consistent basis.
Monitoring everything you put in your mouth is essential on a therapeutic ketogenic diet, especially when you begin. It may not be as important for a modified ketogenic diet. It is most practical to do this with a ketogenic diet app. You enter all the food and beverages you consume, how much you consume, and what time you eat or drink. The app calculates your macros and compares them to your target macros. It allows you to adhere to the diet with the highest potential for success.
Common Mistakes
Because everything is written down, keto can be followed quite easily. There are some mistakes that are common, however, due to the necessary strictness of the diet. It can help you to avoid them or to notice and correct them quickly if you know to look for these ahead of time.
Hidden Carbs
Tracking your macros using an app is the best way to control your carb intake. Even then, it can be easy to over-consume carbs on the keto diet. Here are some good habits to keep carbs in check.
Read labels: Count every carb in food, drinks, and supplements. Know that food and supplement manufacturers can list zero carbs for up to 0.5g of carbs per serving. This can really impact you on keto. So, in addition to looking at the macros on the label, you should also be aware of the ingredients.
Measure portion sizes: Eating too large a meal can spike insulin and throw you out of ketosis, even if you are eating within your macro allowance. Learning how much your food weighs can help you understand how portion size is affecting you. Most people do well with the total calories for the day broken up into two to three meals.
Log all your food: Write down every bite. Meals will probably be easy to remember to log. Anything you pop in your mouth between meals must be noted as well, however, to get an accurate picture. Beverages, too
Too Much Protein
Protein metabolizes into sugar to some extent. So consuming too much protein on a strict therapeutic keto diet can throw you out of ketosis. If you are tracking foods for which you are not entering the protein, you may need to include the protein in the calculation. If you are tracking all your foods well, you might try reducing the protein by 10 g per day.
Too Little Fat
If your ketones are below your target, the first thing to consider is if you are really eating enough fat. Some people find it difficult to ramp all the way up to the planned amount of fat at first. Identify what the issue is. Are you hitting a wall with how much fat you can digest? Are you getting full too quickly? Are you just habitually preparing less fat than is planned on your keto diet? The amount of fat in a keto diet is something both the body and the mind need to adapt to.
Possible Side Effects
When transitioning into ketosis, the body goes through some changes which, if they happen to quickly, can cause some side effects. These are fatigue, headaches, nausea, dizziness, irritability and muscle cramps. Many of these have to do with blood sugar dropping too quickly. Transitioning onto the ketogenic diet over a 5-day period often avoids the risk of these.
Some of these symptoms are related to low electrolytes. In the early weeks of keto, the body is liberating a lot of water that is attached the glucose stored in the liver. Salting the food more than usual, with sea salt, can be very supportive to the transition.
Acetone is one of the ketones the body makes on a ketogenic diet, particularly early in the process. Acetone emits in the breath and can smell like nail polish remover. This is more common during the early weeks of the keto diet and is completely normal and a sign of making ketones. After you are keto-adapted, the body favors making more of the ketone that appears in the blood.
Long-term ketosis, more than a year, can potentially start to show imbalanced energy metabolism, blood pH, and an overly catabolic state. It’s important to keep track of your goals and whether you’ve met them or not so you can take a break from keto after some time. Keeping the breath rate in the 14-18 breaths per minute range is a good way to monitor energy metabolism and blood pH. A breath rate lower than 14 indicates overly alkaline blood. Saliva and urine pHs are good ways to monitor if you are too catabolic. The saliva pH is ideally about 1.0 point above the urine pH.
If the pHs are further apart, the body is getting too catabolic, and it may be time to take a break from keto. In many conditions, like PCOS, the body isn’t catabolic enough, and that’s one way keto is working. But you are looking to bring the body back into balance, not go too far in the other direction.
Who Should Not Immediately Start a Keto Diet
Many people easily take on a keto diet. Some people would be better off avoiding it. If you have any of the following conditions or a subclinical version of them, you will want to avoid a ketogenic diet until the condition is resolved or only do keto under professional guidance.
-
-
- You have low thyroid function. Your body is already having trouble making energy. Trying for ketosis is more likely to backfire in this situation.
- You are overly catabolic. You can gauge this for yourself if your saliva pH is more than 1.0 point higher than your urine pH. The keto diet pushes toward the catabolic state.
- You have elevated estrogen. Energy production is already impaired.
- You have elevated serotonin. Energy production is already impaired.
- You have elevated nitric oxide levels. Energy production is already impaired.
- Your blood is too alkaline. You can gauge this for yourself if your breath rate is less than 14 breaths per minute. Keto will deepen this imbalance.
- You have a diagnosis of primary carnitine deficiency, carnitine translocase deficiency, or carnitine palmitoyl transferase I or II deficiency.
- You have a diagnosis of beta-oxidation defects.
- You have a diagnosis of short-, medium-, or long-chain acyl dehydrogenase deficiency.
- You have a diagnosis of medium- or long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA deficiency.
- You have a diagnosis of pyruvate carboxylase deficiency.
- You have a diagnosis of porphyria.
- You have high liver enzymes.
- You have impaired gut function.
- You have a history of kidney stones or kidney disease.
- You have a history of pancreatitis.
- You have blood chemistry abnormalities.
- You are pregnant or nursing.
- You are extremely physically active. To maintain the same level of performance you may need professional support transitioning to keto.
- You are taking prescription medications. You must consult your pharmacist first as keto can lower blood pressure and blood sugar and may exacerbate the effects of your medications.
-
Seek professional guidance if you are unsure of yourself. Keto can be extremely therapeutic when the benefits outweigh the drawbacks.
The Bottom Line
The keto diet is a powerful self-care tactic that can have strong therapeutic benefits. See if it’s right for you before trying it. Use this guide to learn the basics, gather some cookbooks and a tracking app to plan your meals, go shopping at a diet-specific health specialized grocer for the easiest compliance, and start monitoring your progress.
We can’t wait to help you on your healing way!
Healthy Keto Essentials

Fruits & Veggies

Meat & Poultry

Fishery

Dairy & Alternatives

Bakery

Breakfast & Cereals

Coffee & Tea

Beverage

Nuts & Seeds

Pasta, Rice & Pulses

Cans & Jars

Frozen Food
Herbs & Spices

Home Baking

Ready-to-Eat
Snacks & Treats

Superfoods & Insights